A Schnorr digital signature is a set of algorithms: (KeyGen, Sign, Verify).
Schnorr signatures have several advantages. One key advantage is that when multiple keys are used to sign the same message, the resulting signatures can be combined into a single signature. This can be used to significantly reduce the size of multisig payments and other multisig related transactions.
Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold Signatures - Created by Chelsea Komlo (University of Waterloo, Zcash Foundation) & Ian Goldberg (University of Waterloo).
<aside> 💡 FROST is a threshold signature and distributed key generation protocol that offers minimal rounds of communication and is secure to be run in parallel. FROST protocol is a threshold version of the Schnorr signature scheme.
</aside>
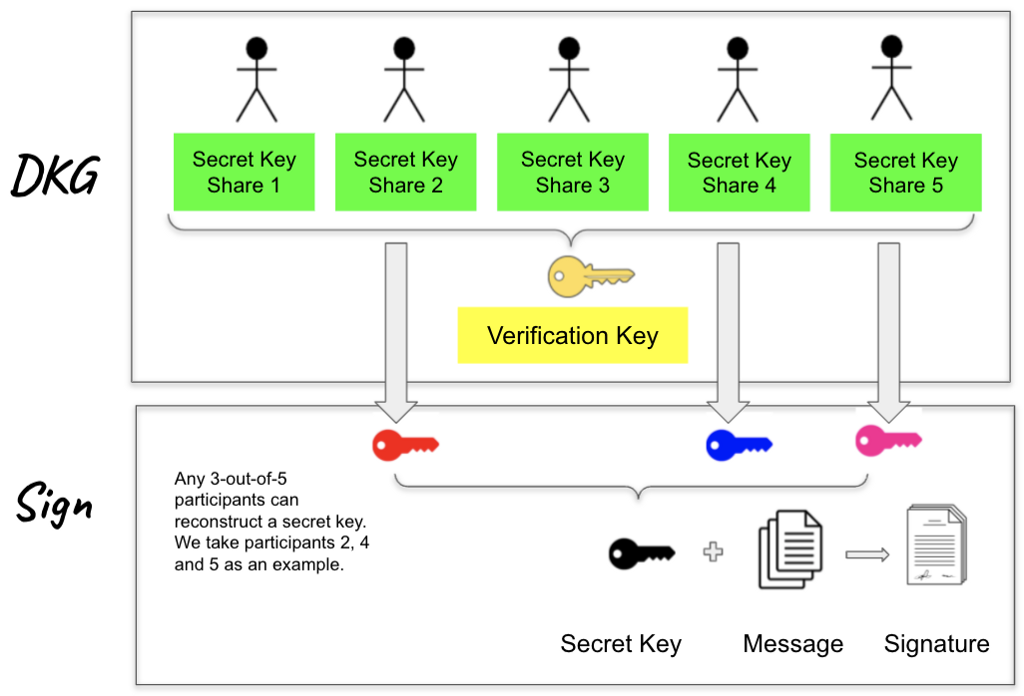
Unlike signatures in a single-party setting, threshold signatures require cooperation among a threshold number of signers each holding a share of a common private key.
What are Threshold Signatures? Chelsea Komlo - Zcon3
Consequently, generating signatures in a threshold setting imposes overhead due to network rounds among signers, proving costly when secret shares are stored on network-limited devices or when coordination occurs over unreliable networks.
Network overhead during signing operations is reduced by employing a novel technique to protect against forgery attacks applicable to other schemes.
FROST improves upon threshold signature protocols as an unlimited number of signature operations can be performed safely in parallel (concurrency).
It can be used as either a 2-round protocol where signers send and receive 2 messages in total, or optimized to a single-round signing protocol with a pre-processing stage.
FROST achieves its efficiency improvements in part by allowing the protocol to abort in the presence of a misbehaving participant (who is then identified and excluded from future operations).
Proofs of security demonstrating that FROST is secure against chosen-message attacks assuming the discrete logarithm problem is hard and the adversary controls fewer participants than the threshold are provided here.
The FROST protocol contains two important components:
First, n participants run a distributed key generation (DKG) protocol to generate a common verification key; at the end, each participant obtains a private secret key share and a public verification key share.
Afterwards, any t-out-of-n participants can run a threshold signing protocol to collaboratively generate a valid Schnorr signature.
